In modern communication, two-way radios are reliable instant communication tools widely used in public safety, industrial operations, outdoor adventures, and commercial activities. With technological advancements, Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) two-way radios are gradually replacing traditional analog radios, becoming the preferred choice for many professional users. This guide provides a comprehensive analysis of DMR two-way radios from the perspective of a professional radio integrator, covering their definition, core advantages, working principles, transmission range, offline operation capabilities, and top brand recommendations. All content is based on ETSI international telecommunications standards and industry best practices, ensuring professionalism and credibility to help you make informed purchasing and deployment decisions.
Introduction: What Are DMR Radios & Their Core Value?
DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) two-way radios are professional wireless communication devices based on digital technology, standardized by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). They use digital signal processing (DSP) technology to convert voice and data into digital formats for transmission, delivering clearer, more efficient communication compared to analog alternatives. Compared to traditional analog two-way radios, DMR radios offer significant advantages in spectrum utilization, anti-interference capabilities, and feature expandability—key reasons for their rapid adoption across industries.
The DMR standard is divided into three tiers to meet diverse needs: Tier I (low-cost personal use), Tier II (conventional professional use), and Tier III (trunked systems for large-scale networks). Among these, Tier II is the most widely used in commercial and industrial scenarios. The global DMR market is growing at an annual rate of approximately 10%, driven by increasing demand for high-quality, secure communication in emergency rescue, construction sites, large events, and logistics operations. Below, we dive into why DMR radios are a smart choice and how they outperform traditional communication tools.
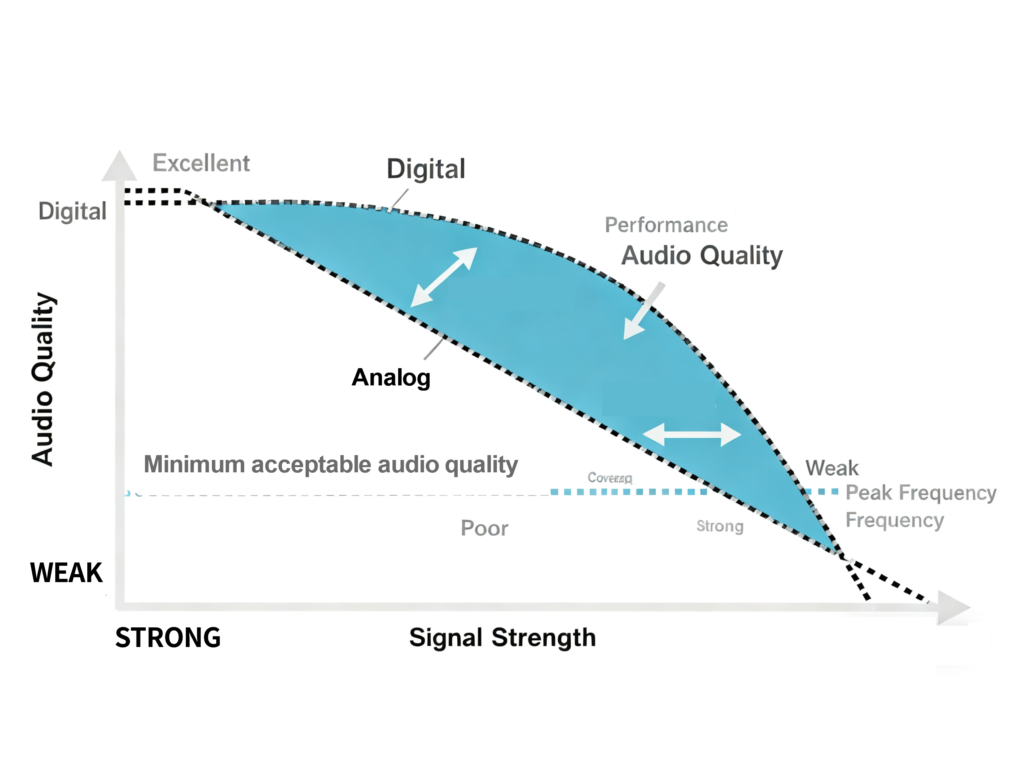
Why Choose DMR Radios? 5 Key Advantages for Professionals
The shift from analog to DMR radios is driven by the unique benefits digital technology brings to professional communication. As experienced radio integrators, we consistently see improvements in operational efficiency and cost savings for users who upgrade to DMR. Here are the core advantages that make DMR radios the top choice for diverse applications:
1. High Spectrum Efficiency (TDMA Technology)
DMR uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology, which splits a 12.5 kHz channel into two independent time slots. This allows two simultaneous conversations on a single channel—doubling capacity compared to analog radios under the same spectrum resources. This is particularly valuable in spectrum-scarce urban areas, where a single repeater can support multiple user groups without interference, reducing infrastructure costs.
2. Crystal-Clear Voice Quality
Digital signal processing, including error correction algorithms and noise suppression, minimizes background noise and signal attenuation. Even in noisy factories, busy construction sites, or remote outdoor environments, DMR radios deliver crisp, intelligible voice quality—ensuring critical information is transmitted accurately. In contrast, analog radios often suffer from distortion and static in weak signal areas.
3. Enhanced Data & Smart Features
DMR radios support a range of data services beyond voice, including text messaging, GPS positioning, and real-time data transmission. These features are game-changers for logistics (tracking vehicle locations), security (sending emergency alerts), and remote operations (sharing sensor data). Many modern DMR models also integrate Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for seamless programming and device connectivity.
4. Longer Battery Life & Security
Efficient digital signal processing reduces standby power consumption, giving DMR radios a 20-30% longer battery life than analog counterparts—critical for shift workers or outdoor teams without easy access to charging. Additionally, built-in digital encryption prevents eavesdropping, making DMR radios ideal for sensitive industries like public safety, government, and finance.
5. Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in DMR radios may be higher than analog devices, their efficiency and low maintenance costs deliver significant long-term returns. For example, fewer repeaters are needed to cover large areas, and dual-mode (digital/analog) compatibility allows gradual upgrades without replacing existing analog infrastructure.
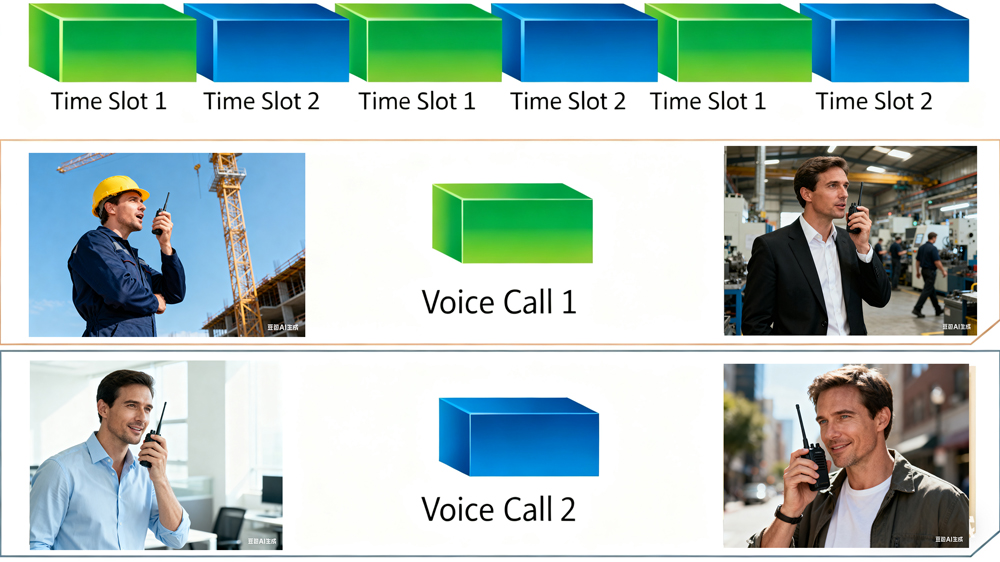
How Do DMR Radios Work? A Simplified Breakdown
The functionality of DMR radios is rooted in digital signal processing and TDMA technology. The entire communication process involves encoding, modulation, transmission, and decoding—ensuring efficient, secure, and reliable connectivity. Understanding these basics helps users maximize device performance. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
1. Voice Digitization
When a user speaks into the radio’s microphone, the analog voice signal is captured and converted to digital data by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). A codec (e.g., AMBE+2) compresses the data to reduce bandwidth usage while preserving voice quality—ensuring efficient transmission.
2. TDMA Time Slot Allocation
The DMR standard divides each channel into two 30-millisecond time slots (Slot 1 and Slot 2). This enables two independent conversations on the same frequency without interference. For example, a dispatch team can use Slot 1 for commands, while field personnel use Slot 2 for status updates—maximizing channel efficiency.
3. Signal Modulation & Transmission
Digital data is converted to radio waves using Gaussian Filtered Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) modulation, which offers strong anti-interference capabilities for variable environments. Signals are transmitted via the radio’s antenna in two modes: direct mode (radio-to-radio communication for short ranges) or relay mode (using repeaters to extend coverage).
4. Reception & Decoding
The receiving radio captures the radio waves, converts them back to digital data via a demodulator, and uses error correction algorithms to fix transmission errors. A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) then restores the data to an analog voice signal, which is played through the speaker.
DMR radios also transmit data (e.g., GPS coordinates, text messages) by encapsulating data in digital frames. All DMR devices adhere to open ETSI standards, ensuring interoperability—radios from different brands can work together in the same network if they comply with the standard.
DMR Radio Transmission Range: What You Need to Know
The transmission range of DMR radios depends on four key factors: device power, environmental obstacles, antenna quality/height, and usage mode. Under ideal conditions (open areas with no obstacles), DMR radios can cover several to tens of kilometers. However, real-world range varies significantly based on the environment. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Key Factors Affecting Range
- Transmit Power: Handheld DMR radios typically have 1-5 watts of power, while vehicle-mounted models range from 10-50 watts. Higher power = longer range: a 5-watt handheld covers 5-10 km in open areas, while a 1-watt model covers 1-3 km.
- Environmental Conditions: Urban areas (buildings, trees, concrete) reflect or absorb signals, reducing range to 1-3 km (direct mode). Rural/maritime areas offer extended range, while rain/snow slightly impacts signal propagation.
- Antenna & Height: High-gain antennas and elevated positions (e.g., rooftop-mounted repeaters) extend coverage. Repeaters can boost range from kilometers to tens of kilometers.
- Usage Mode: Direct mode (radio-to-radio) is limited to short ranges. Relay mode (via repeaters) can cover entire cities or regions.
Typical DMR Radio Range (4-Watt Handheld)
| Environment | Direct Mode Range | Relay Mode Range |
|---|---|---|
| Open Area (e.g., plains, lakes) | 5-10 km | 20-50 km |
| Urban Environment (cities, suburbs) | 1-3 km | 10-30 km |
| Indoor Environment (offices, warehouses) | 0.5-2 km | 5-15 km |
Note: These are estimates—actual range varies by brand, model, and configuration. DMR’s digital technology doesn’t directly increase range, but its error correction maintains quality in weak signal areas, improving effective range. For large-area coverage, use repeaters or high-power vehicle-mounted radios.
Can DMR Radios Work Without the Internet? Yes!
A core advantage of DMR radios is their ability to operate entirely without the internet—making them reliable in remote areas, natural disasters, or situations where internet infrastructure is down. DMR systems rely on radio wave transmission, not internet networks, using dedicated frequencies and repeater networks.
DMR Operating Modes (No Internet Required)
- Direct Mode: Radios communicate directly via designated frequencies—no external equipment needed. Ideal for small teams (e.g., outdoor adventurers, on-site repair crews) and fast, simple communication.
- Relay Mode: Repeaters (fixed devices installed on towers/buildings) receive and retransmit signals to extend range. Repeaters use radio links, not the internet, to cover wider areas. Internet integration is only optional for advanced features (e.g., cross-regional IP-connected repeaters), not basic communication.
Practical use case: Mountain rescue teams use DMR radios in direct mode to stay connected in remote areas with no cell/internet coverage. Digital encryption ensures their communications remain secure from unauthorized access. For most professional needs (construction, security, logistics), DMR radios deliver reliable connectivity without internet dependency.
DMR vs. Other Communication Standards: Which Is Best?
Choosing the right two-way radio requires understanding how DMR compares to other mainstream technologies. Below is a head-to-head comparison of DMR with analog radios, TETRA, and P25—highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases:
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Radios | Low cost, strong compatibility, simple operation | Poor voice quality, low spectrum efficiency, prone to interference | Small teams, basic communication needs, tight budgets |
| DMR | High spectrum efficiency, clear voice, rich data features, moderate cost, dual-mode support | Requires digital-compatible devices, basic setup complexity | Enterprises, industry, public safety (mid-market), logistics, construction |
| TETRA | High security, advanced trunking, complex data support | High cost, closed standards, expensive equipment | Government, emergency services, large critical missions (e.g., military) |
| P25 | Strong interoperability, North American standard, high reliability | Relatively high cost, lower spectrum efficiency | Public safety, government agencies (North America) |
DMR strikes the best balance between cost, functionality, and efficiency for most businesses and organizations. It offers professional-grade features without the prohibitive cost of TETRA or P25, making it the top choice for commercial and industrial users.
DMR Tier I vs. Tier II vs. Tier III: Which Tier Fits Your Needs?
The DMR standard is divided into three tiers, each designed for specific use cases. Below is a simplified comparison to help you choose the right tier:
| Tier | Definition | Frequency Use | Ideal Scenarios | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I | Low-cost, license-free | License-free bands (e.g., 446 MHz) | Personal use, short-range communication | Amateur radio, family camping, small hobby groups |
| Tier II | Conventional professional grade (license required) | Licensed bands (e.g., 400-470 MHz) | Enterprises, industry, commercial applications | Construction sites, hotel management, retail security |
| Tier III | Advanced trunked systems | Multi-frequency relay, IP network integration | Large organizations, critical missions | Public transport, municipal emergency services, large factories |
Tier II is the most popular choice for commercial users, as it balances professionalism and cost-effectiveness. Choose Tier III if you need multi-site connectivity or advanced trunking features for large-scale operations.
Top Recommended DMR Radio Brands & Models (2025)
As professional radio integrators, we recommend the following brands based on market reputation, product performance, and user feedback. All comply with ETSI DMR standards and offer models for diverse needs:
1. Motorola R7
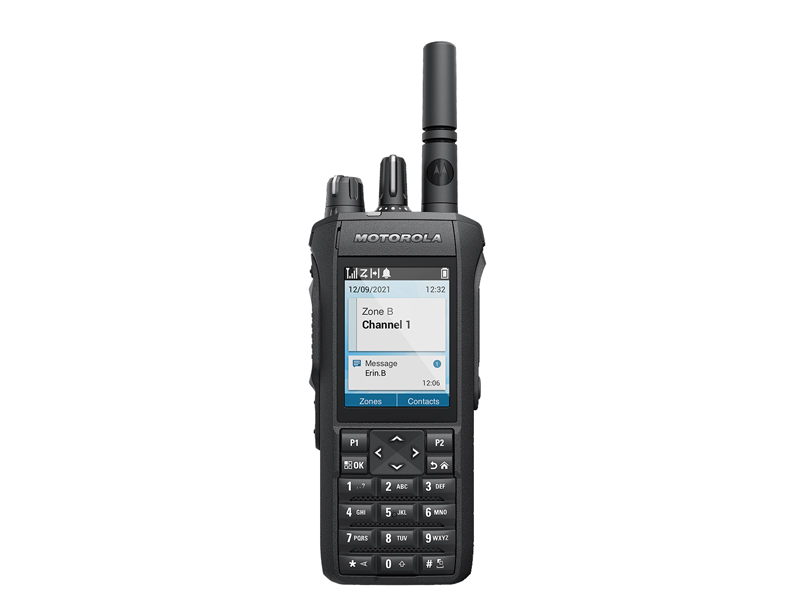

This handheld DMR radio supports dual-mode (digital/analog) operation, built-in GPS, and Bluetooth. With an IP67 protection rating (dustproof/waterproof), it’s ideal for extreme environments (e.g., heavy rain, dusty construction sites). It also offers text messaging and location tracking—perfect for field operations and public safety teams.
2. Hytera HP78 Series
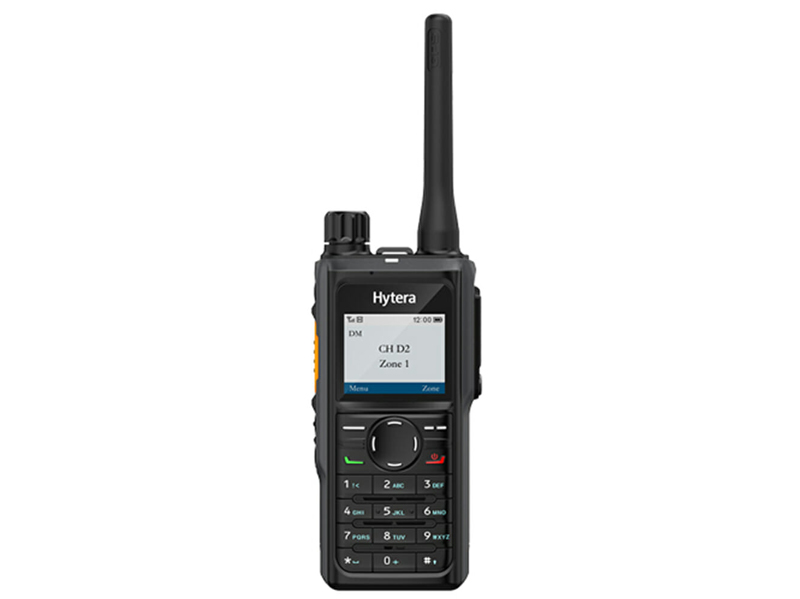

The Hytera HP78 Series stands out for advanced features like Wi-Fi programming, enhanced encryption, and multimedia messaging. Its modular design allows customization (e.g., adding explosion-proof components), making it suitable for complex communication networks in oil & gas, mining, and logistics industries.
Conclusion: DMR Radios Are the Future of Professional Communication
DMR radios represent the gold standard for professional two-way communication, leveraging digital technology to deliver superior spectrum efficiency, voice clarity, and feature versatility. This guide has covered everything you need to know: what DMR radios are, their key advantages, how they work, transmission range, offline capabilities, comparisons to other standards, and top model recommendations.
Key takeaways: DMR radios work reliably without the internet, extend coverage via repeaters, and fit diverse scenarios from construction to emergency response. When purchasing, prioritize ETSI-compliant devices to ensure interoperability and choose the right tier (Tier II for most commercial needs). As a professional radio integrator, we advise aligning your choice with your specific use case—whether it’s small-team communication or large-scale network deployment.
Whether for daily operations, emergency response, or outdoor adventures, DMR radios are your reliable communication partner. If you’re looking to purchase professional DMR radios or build a custom DMR system, contact Alafone for expert advice and tailored quotations.